FTP Counters
1. High level FTP Counters
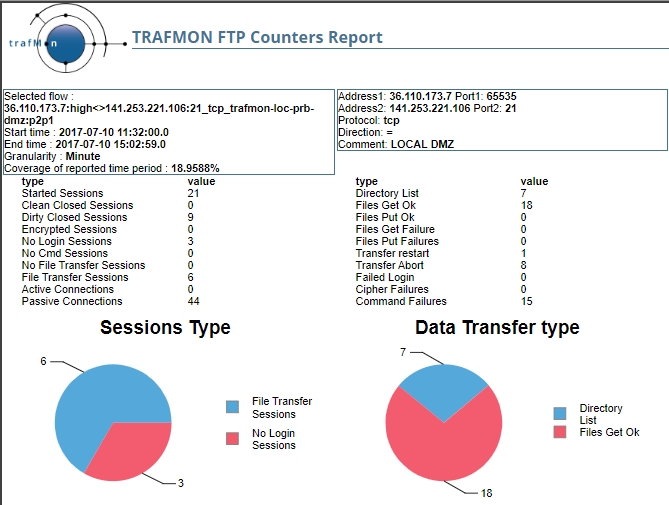
The High level FTP Counters report shows ftp session and transfer statistics.
Clean close is when the user explicitly quit the session unless abruptly closing the underlying TCP connection.
A session starts when its underlying TCP connection is established. When broken at that point, the session is without login (typically used by service monitoring software to see whether the FTP server is available).
Then, if the client doesn’t provide a valid username/password this is a failed login, also counted as no login session, unless the proper user finnaly connects.
When the session is closed just after login, it is said to be a no command session.
Then the user could simply traverse the directory tree, e.g. to check the presence or size of a file, in which case this counts for a no file transfer session.
Of course, it happens that one or more actual file transfer are conducted (or attempted) within a same session. This is counted as a file transfer session.
Each directory listing or (get/put) file transfer induces the establishment of a separated and dedicated TCP data connection. It is said active when the FTP server takes the initiative, or passive when it is the client that makes the data connection.
2. Evolution Counters
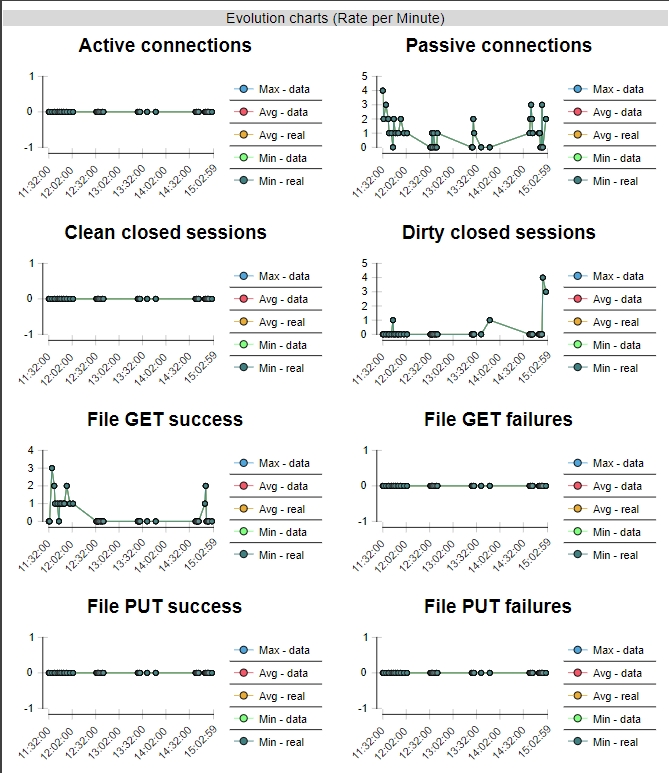
The FTP evolution charts show the time evolution of every above mentioned counter.
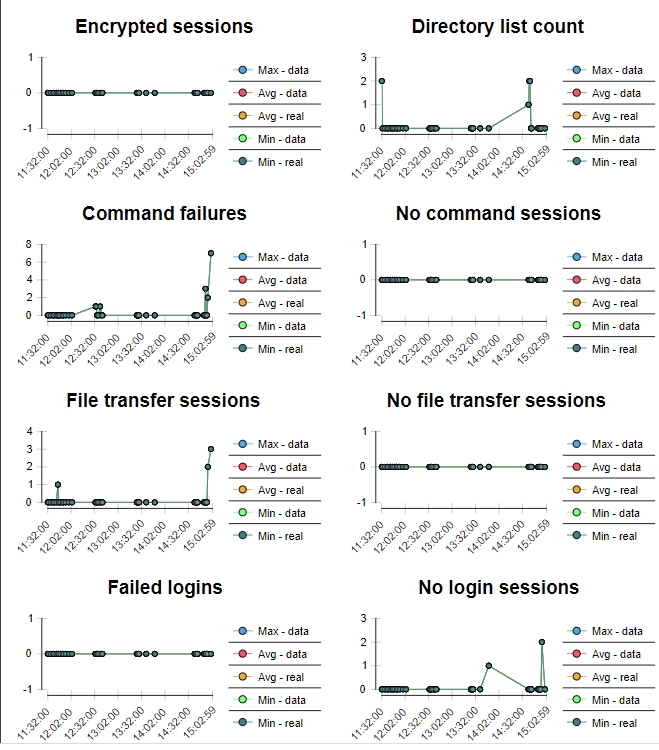
The FTP evolution charts report also shows Encrypted sessions, Directory list count, Command Failure, No command sessions, File transfer sessions, No file transfer sessions, Failed logins and No login sessions.
The FTP evolution charts report also shows Transfer restarts, transfer aborts, started connections and Cipher failures.

